Understanding Fiber Optic Cables by Type and Application
GigaTech Products supplies standard and custom fiber cables for your network and computing application needs. All GigaTech fiber cables are built with Corning glass, offering superior data transmission with outstanding performance characteristics which exceed industry standards. Understanding the specifications and uses of different fiber cables is necessary when planning out the infrastructure of your network.
Single-Mode vs Multi-Mode
Single-Mode Fiber
Single-Mode Fiber consists of a single fiber core which allows only one mode of light to be transmitted at a time. It has a lower dispersion and attenuation which makes it ideal for long distance transmissions. The maximum distance of transmission can reach up to 200km and is dictated by the wavelength of the optical transmission.
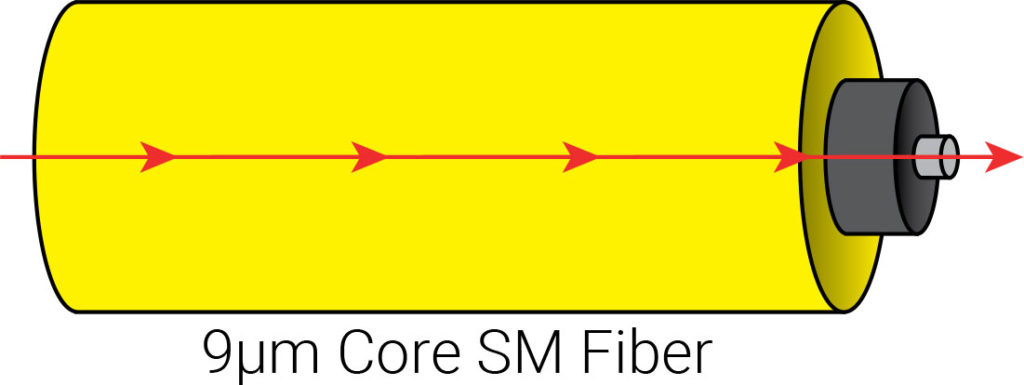
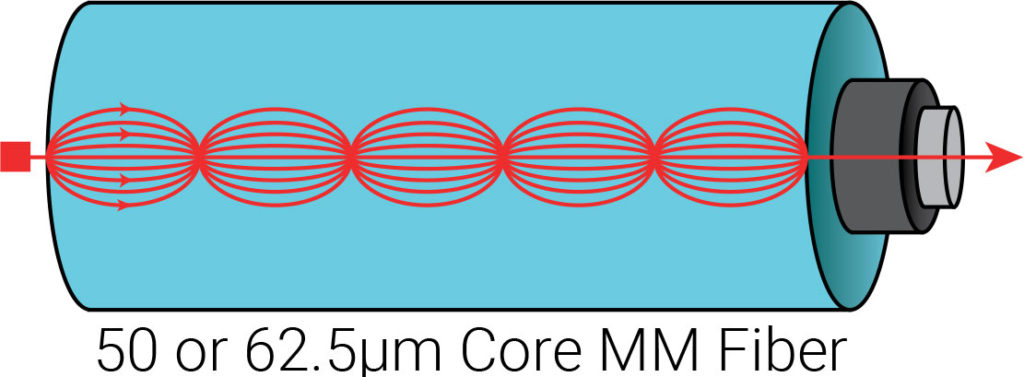
Multi-Mode Fiber
Multi-Mode Fiber utilizes a larger fiber core than its single-mode counterpart allowing multiple modes of light to pass through it simultaneously. Due to higher dispersion and signal attenuation it is only ideal for distances up to 2km and under, dependant on the modal bandwidth.

Multi-Mode Fiber Standards
In order to extend the transmission distance and capacity of multi-mode fiber types the industry has introduced the OM1, OM2, OM3, and OM4 standards. These differ by core and cladding diameters and are each rated by minimum modal bandwidth as dictated by the ISO 11801 Standard.
OM1 & OM2 vs OM3 & OM4
OM1 and OM2 work with LED-based equipment that can send hundreds of modes of light down the cable, while OM3 and OM4 fiber are optimized for laser (VCSEL) based equipment that uses fewer modes of light. LEDs cannot be turned on/off fast enough to support higher bandwidth applications, while VCSELs are capable of modulation over 10 Gbit/s and are used in many high-speed networks. For this reason, OM3 and OM4 are the multimode fibers included in the 40G and 100G Ethernet standard. OM1 and OM2 are used for 1G and are not suitable for today and tomorrow’s higher-speed networks.
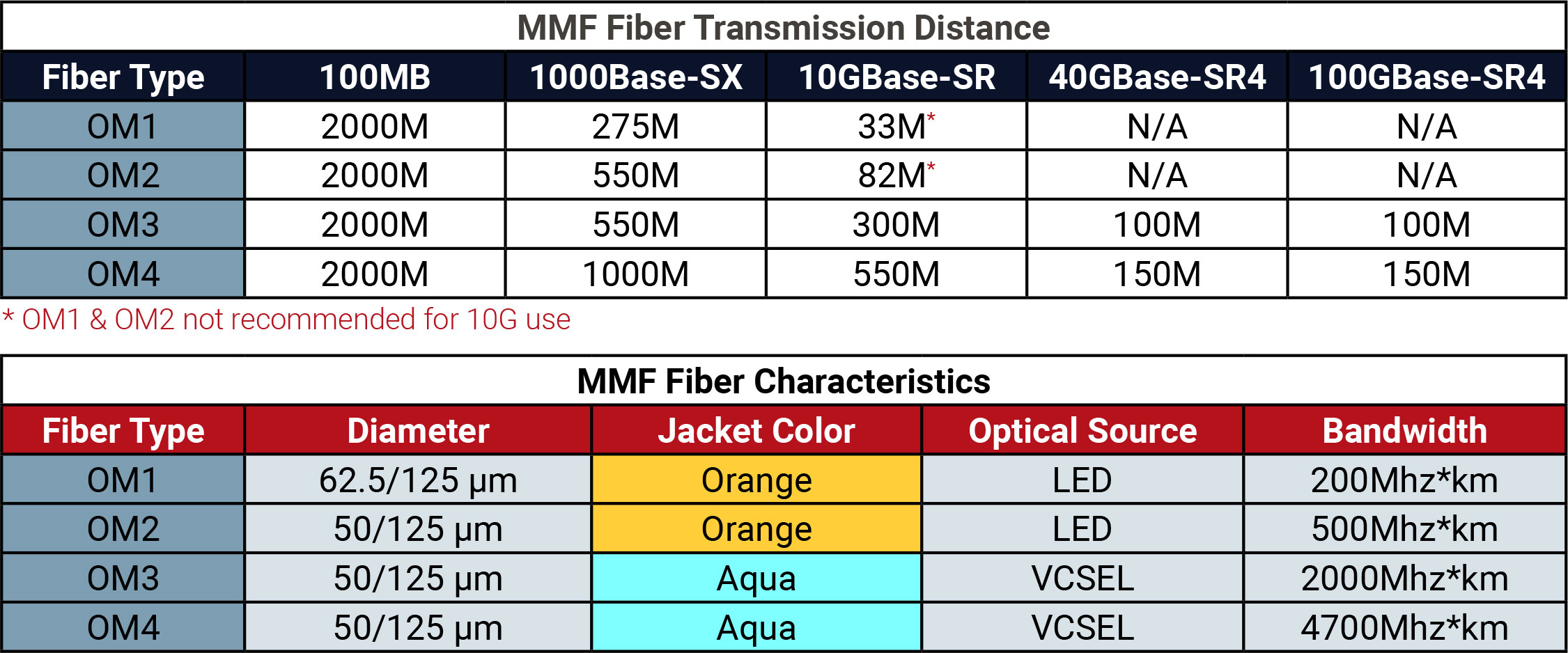
The characteristics in the tables above highlight the differences between the 4 fiber types.
Core Diameter: The center of the fiber, or the Core, plays a big role in the quality and distance the signal can travel through the fiber. In general, the smaller the core the farther the optical signal (light pulse) will go before it needs to be regenerated. OM1 cables utilize a larger core size of 62.5µm while OM2, OM3, and OM4 have a smaller 50µm core. All utilize a 125µm jacket.
Jacket Color: OM1 and OM2 MMF are generally defined by an orange jacket. OM3 and OM4 are usually defined with an aqua jacket.
Optical Source: OM1 and OM2 commonly use LED light source. However, OM3 and OM4 usually use 850 nm VCSELs.
Bandwidth: The maximum signaling rate for a given distance and is measured as Megahertz over 1 Kilometer, expressed as MHz*km. It refers to how much data a specific fiber can transmit at a given wavelength. At 850 nm the minimal modal bandwidth of OM1 is 200MHz*km, of OM2 is 500MHz*km, of OM3 is 2000MHz*km, of OM4 is 4700MHz*km.
