Network Transceiver Maintenance
Inspection and Cleaning Procedures for Fiber-Optic Connections
The reliability and effectiveness of optical transceivers and fiber optic cables depend not only on their quality but also on how well they are maintained. Regular inspection and cleaning of these components are crucial for ensuring high performance levels of the whole network system. Even the tiniest speck of dust can significantly disrupt signal transmission and cause reduced data quality, increased latency, and connectivity problems. Regular and proper cleaning of fiber optic cables and transceivers ensures long-term reliability and performance and prevents costly repairs, downtime, and network disruptions.
Signs an optical transceiver may be contaminated
Performance Monitoring
Signs of contamination usually exhibit themselves in the form of performance degradation
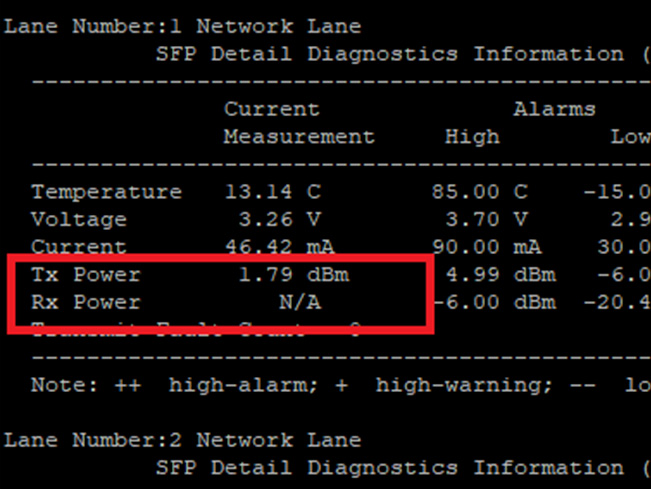
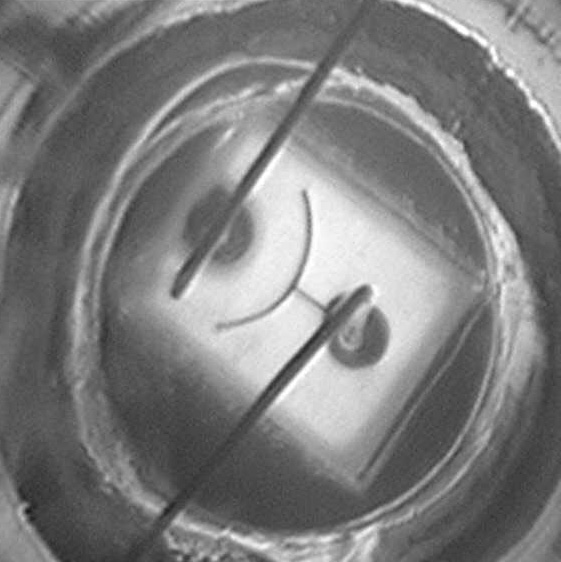
Example picture features an RX Lens too contaminated to pass data.
Guide Menu
Transceiver Inspection & Diagnosis
Optical transceivers require regular inspection and cleaning to ensure optimal performance. The cleanliness of fiber optic connections is crucial because even the smallest particle of dust can cause problems for your signal transmission.
Contaminated Transceiver Lens
Clean Transceiver Lens
Why is maintenance important?
Even if a transceiver and fiber cable were cleaned and properly inspected upon original installation, there are still ways in which the connectors can acquire contamination over time, even if the cable has never been removed. Here are some potential causes:
Airflow
Wear and Tear
Condensation
Enclosures
Airborne Contaminants
Microscopic Particles
Degradation of Materials
Diagnosing Transceiver Contamination
Visual Inspection
Physical Environment Monitoring
Optic Baseline Monitoring
How To Clean a Transceiver

• Non-abrasive cleaner (air duster)
• Use a dry, lint-free cleaning swab.
• Insert the swab into the transceiver's receptacle.
• Rotate the swab gently for a few turns and then remove.
• Discard the swab after one use.
• Before handling any module, confirm that it's powered down and treat each module delicately.
• Only use Clean Dry Air (CDA) or a trusted source of canned compressed air.
• While using compressed air, keep the can in a vertical position. Angling it might cause unwanted liquids to be discharged with the air.
General Guide For When to Clean
Transceiver Maintenance Products
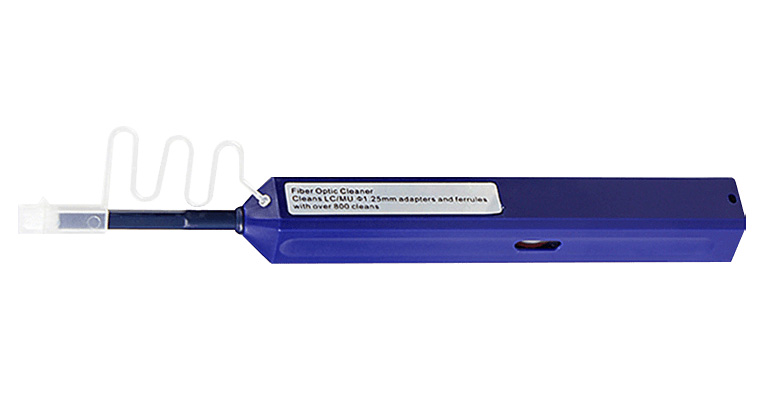

Designed for cleaning LC and MU type connectors, this fiber cleaner can easily remove dirt, dust, oil and grease from an optical fiber adaptor. With the ability to each into the entire area within the connector, it makes cleaning of the ferrule endface a simple task with the push of a button.
For Fiber Connectors (LC/MU):
For Transceiver / Fiber Patch Connection (LC/MU)
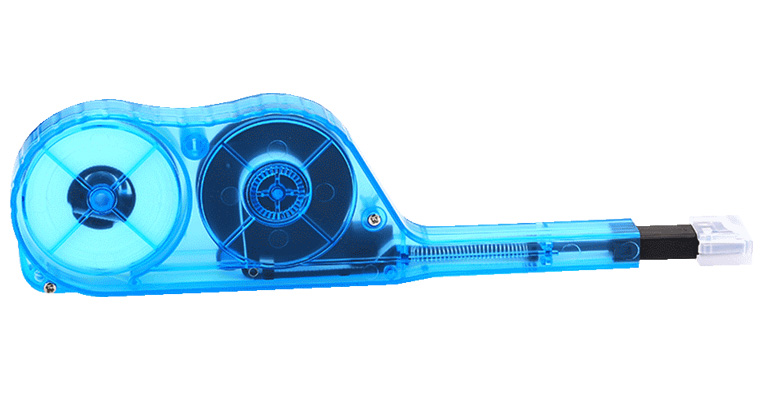
This push-type cleaner is specifically designed for the cleaning of ferrule end-faces in MTP/MPO adapters. With the ability to clean all 8/12/24 fibers simultaneously it is a time and cost efficient tool for the maintenance of fiber cables. This cleaner can clean both exposed jumper ends as well as connectors embedded in the adapter.

